Brass Instruments
- Two basic families with rather little
difference in tone
- Straight tubes with some conical or flared
sections
- Trumpet, Trombone, French Horn
- Brighter sound. Used in orchestras where
brightness is needed to cut through mass of
other instruments.
- Conical tubes with some flared or otherwise
slightly altered sections
- Cornet, Flugel horn, alto horn, baritone,
Euphonium, Tubas
- Mellower sound. Used in ensembles (brass
bands, silver bands) where the sound blends
better than trumpets etc. would.
- Lip reed
- Player can alter tension in lip over a
very wide range. Gives the player control
over natural frequency and over Q not
available to other reed players.
- Mouthpiece
- Surface to rest lips, resonator chamber
with a sharply constricted opening, conical
tube to match to bore of instrument
- Body tube
- Basically straight or basically
cylindrical according to family.
- Length determines pitch of instrument. As
usual, the longer the tube the larger the
bore to allow low frequencies to get
out.
- Bell
- Couples tube to the outside world.
Open or Closed tube?
- Bugle calls show that the available notes
from a fixed length tube form a complete
harmonic series (missing the fundamental)
- Lip reed must operate into a high impedance,
high pressure anti-node of the pipe and should
give an incomplete series!
- Flaring bell alters the effective length of
the tube for different frequencies and alters
the pattern of partials.
- The Bell
- Produces a high-frequency cut-off as we
have seen in woodwinds.
- Makes tube have different length for low
frequencies, which reflect early in the bell,
and high frequencies, than high, which travel
somewhat further before reflecting.
- Effect is to raise lower partials
relative to upper ones, altering the 1, 3, 5,
7, relationship.
- The Mouthpiece
- Has natural "popping" frequency around
850Hz. Broad resonance.
- Extra volume of mouthpiece pulls down
some of the upper partials.
- By itself it does not strengthen the
lower resonances enough to make them sharp,
can still slide note around with the
lip.
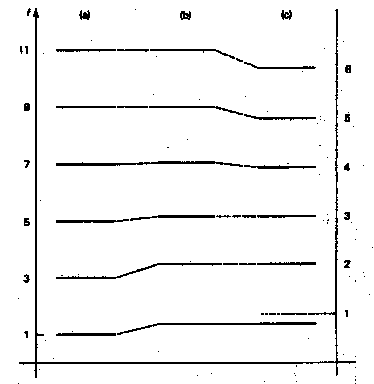
Effect of Bell on Pressure
Combined Effect
- Raises lower modes
- Lowers upper modes
- Result is nearly harmonic set of modes
except for the lowest
- Lowest mode is significantly out of tune
with others and does not give an easily playable
note.
Resulting Brass Modes
Changing the Note
- Have to alter length of tube. Two methods
available
- Slides/Valves change physical length of tube
- Trumpet, French Horn, all the Cornet/Tuba
family use valves.
- Trombone and rare slide trumpet use a
slide.
- Sound always comes from complete tube
so that tone color is quite constant.
- Can only put into a straight section
of tube!
- Holes can shorten acoustic length of tube
- Cornett (2 T's), Serpent use simple
holes
- Keyed bugle, Ophicleide use keywork
- Tone color is much less even over
range. Obsolete.
 |
Physics at Hamilton |
|


